Previous
Boost Your Digestive System to Help Your Liver
Next
The 5 Best Foods for Your Liver
4 Warning Signs of Liver Cancer to Watch Out For
Find out the signs of – as well as risk factors for developing – liver cancer.
The liver is the largest organ in the body, filling the upper right abdomen under the rib cage. The liver has many functions, including the filtering of blood and elimination of toxic substances such as medication and chemicals; the removal of old blood cells; digestion of fats (lipids), carbohydrates and proteins; production of bile for digestion; storage and management of glycogen (sugar) in the blood stream; and the production of the proteins necessary for clotting.
When liver function is compromised, almost every other system in the body is affected and overall health begins to suffer. There are many conditions that affect liver function, just as liver function – or lack of function – affects most normal bodily functions. When the liver cells become damaged and scarred (cirrhosis), tumors begin to form and develop into cancer.
Types of Liver Cancer
There are two primary types of liver cancer:
- Hepatocellular carcinoma – the most common type of adult primary liver cancer.
- Cholangiocarcinoma – cancer in the bile ducts.
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the world and is typically diagnosed in adults around age 50, but can occur in children and younger adults as well. Tests for hepatocellular carcinoma include a liver biopsy, an abdominal CT scan or ultrasound, liver enzymes test (liver function), an MRI of the liver, or a serum alpha fetoprotein blood test [Alpha fetoprotein (AFP) is a protein produced by the liver].
Treatment and prognosis will depend largely on tumor size, number of tumors and degradation of liver cells and function. Tumors may develop as one large tumor or several smaller ones. HCC develops when the cells in the liver replicate at a higher rate, forming tumors which impact liver function. This is typically due to conditions that attach the liver cells such as hepatitis infections, obesity which forces the liver to overwork, or excessive exposure to chemicals, medications or alcohol consumption which overtaxes liver cells.
Other types of cancers may metastasize and begin to grow in the liver, but they are named for the types of cancer they came from. These types of cancer are not considered primary liver cancers.
Signs of Liver Cancer
The liver is responsible for many functions in the body, therefore when it is not functioning normally, many systems are affected. Fatigue, fever, a swollen abdomen, nausea and diarrhea are common symptoms that the liver is in trouble.
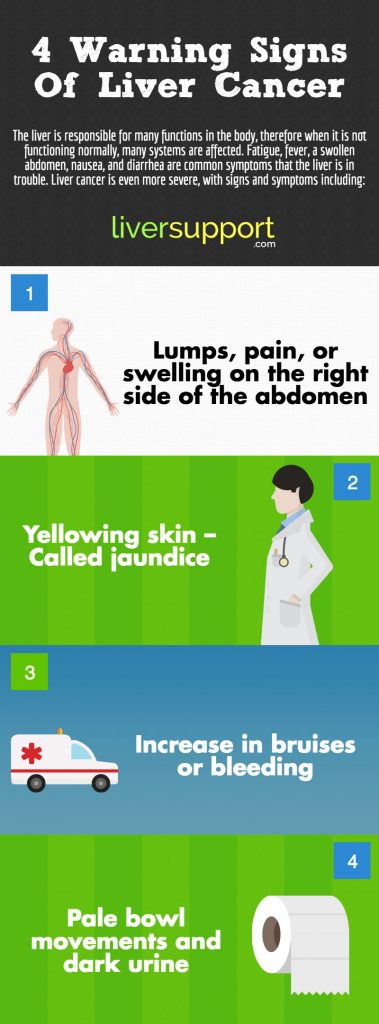
Liver cancer is even more severe, with signs and symptoms including:
- Lumps, pain or swelling – Any lumps, pain or swelling on the right side of the abdomen just under the rib cage or under right shoulder blade may indicate a serious liver condition, including HCC tumors forming in the liver.
- Yellowing skin – Called jaundice, yellowing skin indicates there is a buildup of bilirubin in the blood because the liver is not filtering out the old red blood cells and the bilirubin produced as the old red blood cells break down in the liver.
- Bruising or bleeding – When the liver function slows, or the liver fails, it is unable to produce the proteins necessary to produce clotting. This results in an increase in bruising or bleeding in the entire body.
- Pale bowel movements and dark urine – While jaundice is usually detected by the yellowing of skin (and eyes), dark urine and light stools also indicate that bilirubin is either not being broken down by the liver or the liver is unable to remove it from the body because function is impaired.
Risk Factors for Liver Cancer
- Hepatitis A, B or C infections – hepatitis damages liver cells resulting in scaring, or cirrhosis, over time
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
- Cirrhosis resulting from several conditions, which may include chronic alcohol consumption, Hepatitis, NAFLD
- Hemochromatosis – a condition in which the body stores too much iron in the liver, heart and pancreas
- Obesity – the liver must store excess amounts of glucose as body fat, and fat accumulates in the liver impairing liver function. This results in NAFLD and eventually cirrhosis; left unchecked it can result in cancer.
If you are experiencing any signs or symptoms of liver failure, it is vital that you visit a qualified physician to evaluate the condition. Liver disease and cancer can significantly impact health overall and needs to be taken very seriously.
American Cancer Fund. (2016). What is liver cancer? American Cancer Fund. Retrieved on 9/15/16 from https://www.americancancerfund.org/cancer-types/liver-cancer/?gclid=Cj0KEQjwjem-BRC_isGJlJ-0h-MBEiQAbCimWDxon1Pt8QLR_0wmGlXWkYLLtWGEXVyECKEVjSO7uaoaAm4l8P8HAQ.
Medline Plus. (2016). Liver cancer - hepatocellular carcinoma. Medline Plus. Retrieved on 9/15/16 from https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000280.htm.
NCI. (2016). Adult Primary Liver Cancer Treatment (PDQ®)–Patient Version. National Cancer Institute. Retrieved on 9/15/16 from https://www.cancer.gov/types/liver/patient/adult-liver-treatment-pdq.
NIH. (2016). Cirrhosis. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Disease. Retrieved on 9/15/16 from https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/health-topics/liver-disease/cirrhosis/Pages/facts.aspx.






That’s why it’s really important to keep our liver healthy as much as we take care of the other organs of our body to prevent it from diseases like cancer. Anyway, here are some things you can do to keep your liver healthy as suggested by alternative cancer treatment center in Arizona, New Hope Unlimited:
*Limit alcohol intake
*Eat a healthy diet
*Exercise regularly
*Manage your medications
Just remember the key to having a healthy liver is by having a healthy lifestyle. Strive to be healthier today and make choices that you will be thankful for in the future.
I’m on a fat free diet, had hepc from service back in 60’s went to cancer, since on fat free diet lost 20 lbs in 3 months, body is getting adjusted, still go Baylor Medical in Houston every other month,VA sent blood for HEPC testing may have returned will get results 2 weeks Viral Load