Previous
What Is the #1 Food that Causes Liver Disease?
Next
Can Sitting Too Much Harm Your Liver?
How Does Berberine Benefit Liver Health?
According to research published in the journal Phytotherapy Research, as well as Nutrients, berberine may benefit liver health. Find out how!
Liver health is a concern for many, with 4.5 million adult Americans having been diagnosed with liver disease and another 80 to 100 million likely having fatty liver disease yet not realizing it. (1) Maintaining a healthy weight, limiting alcohol, and avoiding toxins are all ways to help this organ function as well as it can. According to research, berberine may be beneficial as well.
What Is Berberine?
Berberine is an isoquinoline alkaloid found in a variety of plants, including barberry, goldenseal, and Oregon grape. It has been used in traditional Chinese medicine for centuries because it has both antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties. (2)
Potential benefits of berberine include: (3)
- Lowering blood sugar levels
- Reducing cholesterol
- Preventing urinary tract problems (infections and inflammation)
- Easing digestive issues
- Aiding in weight loss
- May reduce colorectal polyps, which can be a precursor to colon cancer
These reasons alone make berberine a substance that helps promote optimal health. However, studies have also shown that it may also be good for liver health specifically.
Research on Berberine and Liver Health
A 2021 review of the literature published in the journal Phytotherapy Research indicates that berberine helps protect the liver, in part, by regulating signaling pathways that play a role in liver disease. (4) Some of the pathways it appears to modulate are the:
- Akt/Fox02 pathway, which plays a role in insulin and growth factors
- PPAR-γ pathway, which controls how the body uses fat and sugar
- Nrf2 pathway, which regulates genes used in detoxification and elimination
- AMPK pathway, which plays a role in energy production
- mTOR pathway, which regulates cell metabolism, growth, and survival
A 2022 review in Nutrients adds that berberine is “one of the most promising” bioactive compounds proposed to treat non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). (5) Now known as metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), this condition is characterized by the buildup of fat in the liver not associated with the consumption of alcohol.
This second review explains that berberine has a positive effect on the liver by inhibiting lipogenesis and gluconeogenesis (the way the body processes fatty acids and glucose, respectively), also improving insulin resistance and lipid profiles, and regulating the gut microbiome.
How to Get Berberine in Your Diet
Berberine is not a substance that is found in foods we normally eat. Instead, it comes from various parts of the plants that contain it, where it can be found in these plants’ roots, stems, and bark. This makes dietary supplements the best method for getting berberine in your diet.
The National Library of Medicine reports that berberine dosages at 1.5 grams or below are generally safe when taken orally. (6) Additionally, some people experience gastrointestinal effects when taking it, including diarrhea, gas, and an upset stomach. These effects often go away as your body gets used to the supplement. Reducing the dosage can help as well. (7)
Berberine should not be taken by individuals who are pregnant or breastfeeding, as well as newborns as it is likely unsafe for these demographics. It may also interact with certain medications. (6) So, talk with your healthcare provider if you are taking any other prescription drugs, over-the-counter medicines, or dietary supplements to ensure that taking berberine is safe for you.
If You’re Interested…
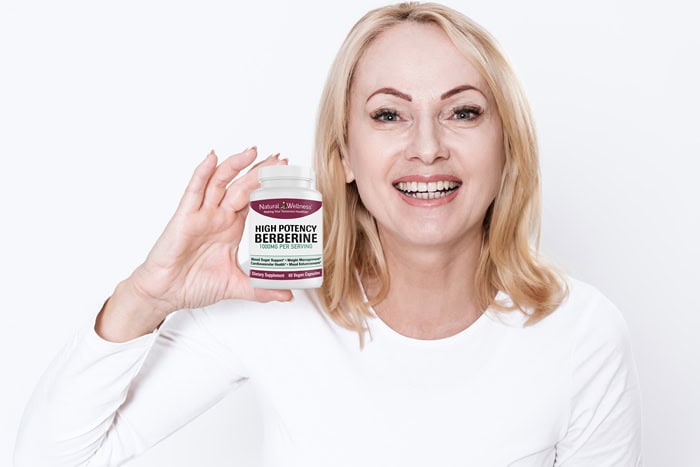
If you’re interested in taking berberine, Natural Wellness offers a High Potency Berberine supplement which supplies 1,000 mg (or 1 gram) per two-capsule serving. This product is also gluten free, non-GMO, and safe for people following a vegan diet.
(1) American Liver Foundation. (2023, September 11). How Many People Have Liver Disease? Retrieved June 13, 2024, from https://liverfoundation.org/about-your-liver/facts-about-liver-disease/how-many-people-have-liver-disease/
(2) Ai, X., Yu, P., Peng, L., et al. (2021, November 02). Berberine: A Review of Its Pharmacokinetics Properties and Therapeutic Potentials in Diverse Vascular Diseases. Frontiers in Pharmacology. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.762654
(3) Conklin, L. (2021, May 14). 6 Potential Benefits of Berberine You Should Know About. Retrieved June 13, 2024, from https://naturopathic.org/news/565580/6-Potential-Benefits-of-Berberine-You-Should-Know-About.htm
(4) Bansod, S., Saifi, M., Godugu, C. (2021, May 31). Molecular Updates on Berberine in Liver Diseases: Bench to Bedside. Phytotherapy Research. doi:10.1002/ptr.7181
(5) Koperska, A., Wesołek, A., Moszak, M., Szulińska, M. (2022, August 23). Berberine in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease—A Review. Nutrients. doi:10.3390/nu14173459
(6) National Library of Medicine. (2024, February 22). Berberine. Retrieved June 13, 2024, from https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/natural/1126.html
(7) Cleveland Clinic. (2023, June 18). What to Know About Berberine: Benefits, Uses and Side Effects. Retrieved June 13, 2024, from https://health.clevelandclinic.org/berberine-for-insulin-resistance-weight-loss







