Previous
Limes Are Sublime for Liver Health
Next
The Advantages of Consuming Protein for Liver Health
Understanding Free Radicals and Their Impact on the Liver
Learn about the influence oxidation, free radicals and antioxidants have on those with liver disease.
Oxidation is a natural process that ensures the cells of our body are continuously evolving. While oxidation’s harmonious cycle of cell birth and cell death is nature’s way of keeping healthy via renewal, this process creates potentially damaging free radicals. According to most experts in anti-aging and chronic disease prevention, stopping the chain reaction created by free radicals is the so-called fountain of youth.
For those with any type of liver disease, preventing oxidative damage in the liver is a necessity for halting liver disease progression and staying healthy.
What Is Oxidation?
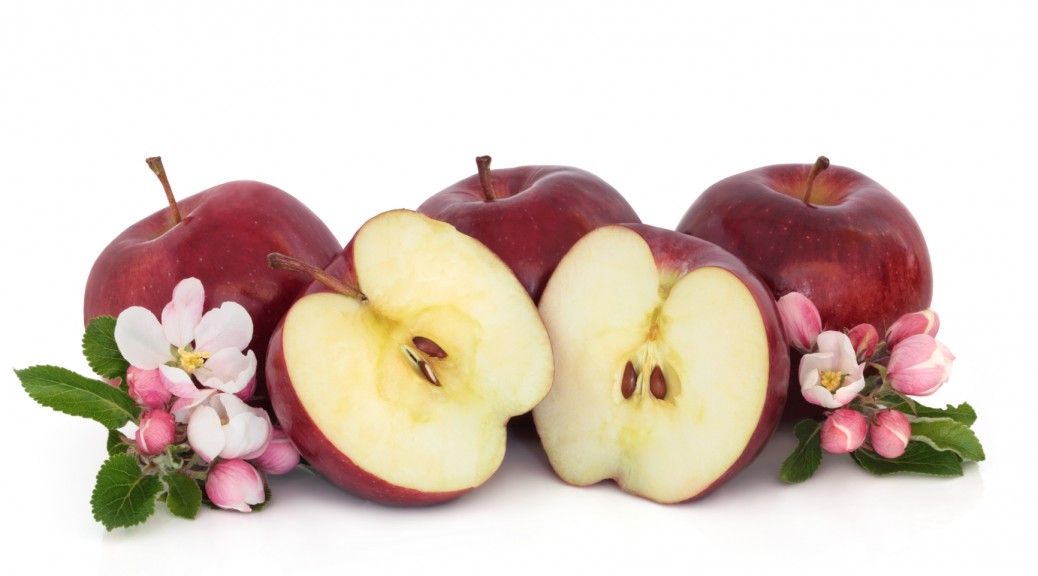
Oxidation is the chemical reaction that occurs when oxygen interacts with cells. A visible example of oxidation is the discoloration that happens soon after an apple is sliced. From a chemical perspective, oxidation describes an atom’s loss of electrons. Electron loss causes the atom affected to change, such as the degradation evident in a sliced apple.
When an oxidizing agent attaches to an atom or molecule, it steals electrons. The result of this theft is the creation of a free radical, a molecule or atom that has an unpaired electron in its outer orbit. Some types of atoms oxidize easily – they lose electrons more easily than others.
Learn how N-acetyl cysteine helps protect your liver from oxidation in the article, “Liver Antioxidants – What to Pair with NAC.”
What are Free Radicals?
Free radicals are very unstable, highly reactive molecules. They are perpetually on the hunt to steal an electron from the nearest stable atom. When a recently attacked atom loses its electron(s) to a free radical, it then becomes unstable and a free radical itself. This process can begin a chain reaction of instability and electron theft, leading to the disruption of normal living cells.
In the body, the domino effect of free radicals can injure cells, including damaging the DNA. When a cell’s DNA changes, it mutates – potentially allowing it to quickly grow and reproduce abnormally. In the liver, an unchecked, free radical chain reaction can lead to fibrosis, cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Normally, free radicals are an essential element to staying healthy. Our cells purposefully release a burst of free radicals to disable infection when we become infected with a bacterium, virus, fungi or parasite. The creation of free radicals is a standard component of human physiology, and is generally not much of a problem. In a healthy individual, free radicals are kept under control by antioxidants.
What are Antioxidants?
Antioxidants are chemicals that prevent oxidation by free radicals, minimizing cellular damage. The body manufactures some antioxidants, while others come from food or supplements. Most brightly colored fruit and vegetables, whole grains, nuts and legumes contain antioxidants, forming the backbone of anti-aging, anti-cancer diets.
The effectiveness of antioxidants is appreciated by comparing freshly sliced apple pieces; one that is plain, the other with lemon juice squeezed over it. The plain apple slice will start to degrade and brown quickly, while the apple with lemon juice will take much longer to change color. The delaying of oxidation occurs with the latter apple slice because lemon juice is rich in Vitamin C – a potent antioxidant.
The liver benefits from antioxidants in the same way that a sliced apple is defended by lemon juice. Consuming a wide variety of antioxidants can minimize the liver cell damage that characterizes liver disease.
Via smart food choices and supplementation, an abundance of antioxidants can prevent oxidation and stop a free radical chain reaction. Thus, someone with liver disease who consumes enough antioxidants can successfully ward off disease progression and prevent the development of liver cancer.
http://study.com/academy/lesson/what-is-oxidation-definition-process-examples.html, What is Oxidation – Definition, Process and Examples, Elizabeth Wyman, Retrieved March 15, 2015, Study.com, 2015.
http://www.consumerhealth.org/articles/display.cfm?ID=19990303172533, Free Radicals: A Major Cause of Aging and Disease, Hari Sharma, MD, Retrieved March 9, 2015, Consumer Health Organization of Canada, 2015.
http://www.drweil.com/drw/u/QAA400537/Stumped-by-Oxidative-Stress.html, Stumped by Oxidative Stress?, Andrew Weil, MD, Retrieved March 15, 2015, Weil Lifestyle, 2015.
http://www.liverdoctor.com/antioxidants-free-radicals/, Antioxidants and Free Radicals, Retrieved March 9, 2015, Liver Doctor, 2015.
http://www.webmd.com/food-recipes/how-antioxidants-work1?page=1, How Antioxidants Work, Jeanie Lerche Davis, Retrieved March 9, 2015, WebMD, LLC, 2015.






